摘要:北京时间3月12日下午,谷歌人工智能AlphaGo与韩国棋手李世石今日进行了第三场较量,最终AlphaGo战胜李世石,连续取得三场胜利。
随着又一次的人工智能与人类智能的世纪大战,我们不禁要思索,人工智能,是在呼唤上帝还是在召唤恶魔?此时正是时候研究一下人工智能相关理论,而本文主要论述计算机科学与技术专业大三下专业课《人工智能》第一个实验算法。
关键字:人工智能,搜索问题,树的深度优先搜索
The Missionaries and Cannibals Problem
Abstract: Beijing time on March 12 in the afternoon, Google AlphaGo and artificial intelligence, the third field of the south Korean chess player lee se-dol today, finally beat lee se-dol AlphaGo, won three consecutive victory.
Again, as the century of artificial intelligence and human intelligence war, we can not help but to think, artificial intelligence, in calling upon god or summon demons? Now is the time to study the related theory, artificial intelligence, this paper mainly discusses the computer science and technology under the junior in professional class "artificial intelligence" in the first experiment algorithm。
Keywords: artificial intelligence, search, depth first search tree
1.问题重述
在河的左岸有N个传教士、N个野人和一条船,传教士们想用这条船把所有人都运过河去,但有以下条件限制:
(1)修道士和野人都会划船,但船每次最多只能运K个人;
(2)在任何岸边野人数目都不能超过修道士,否则修道士会被野人吃掉。
假定野人会服从任何一种过河安排,请规划出一个确保修道士安全过河的计划。
2.问题分析
2.1约束条件:
① M≧C 任何时刻两岸、船上都必须满足传教士人数不少于野人数(M=0时除外,既没有传教士)
② M+C≦K 船上人数限制在K以内
2.2求解:
传教士与野人全部安全渡到对岸的解决方案
3.求解过程
3.1变量假设:
设N=3,K=2(三个M和三个C,每次渡河二人以下)
L:左岸,R:右岸,
B:是否有船(0:无船,1:有船)
3.2状态表示
定义:用三元组(ML,CL,BL)表示左岸状态,其中:
0≦ML,CL≦3,BL∈{0,1}
如:(0,3,1)表示左岸有三个野人,船在左岸。
从(3,3,1)到(0,0,0)的状态转换
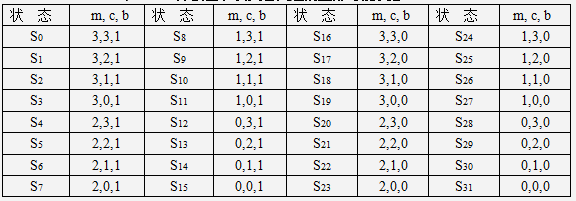
状态空间:32 种状态,其中:
12种不合理状态:如(1,0,1)说明右岸有2个M,3个C;
4种不可能状态:如(3,3,0)说明所有M和C都在左岸,而船在右岸
∴可用的状态共16种,组成合理的状态空间
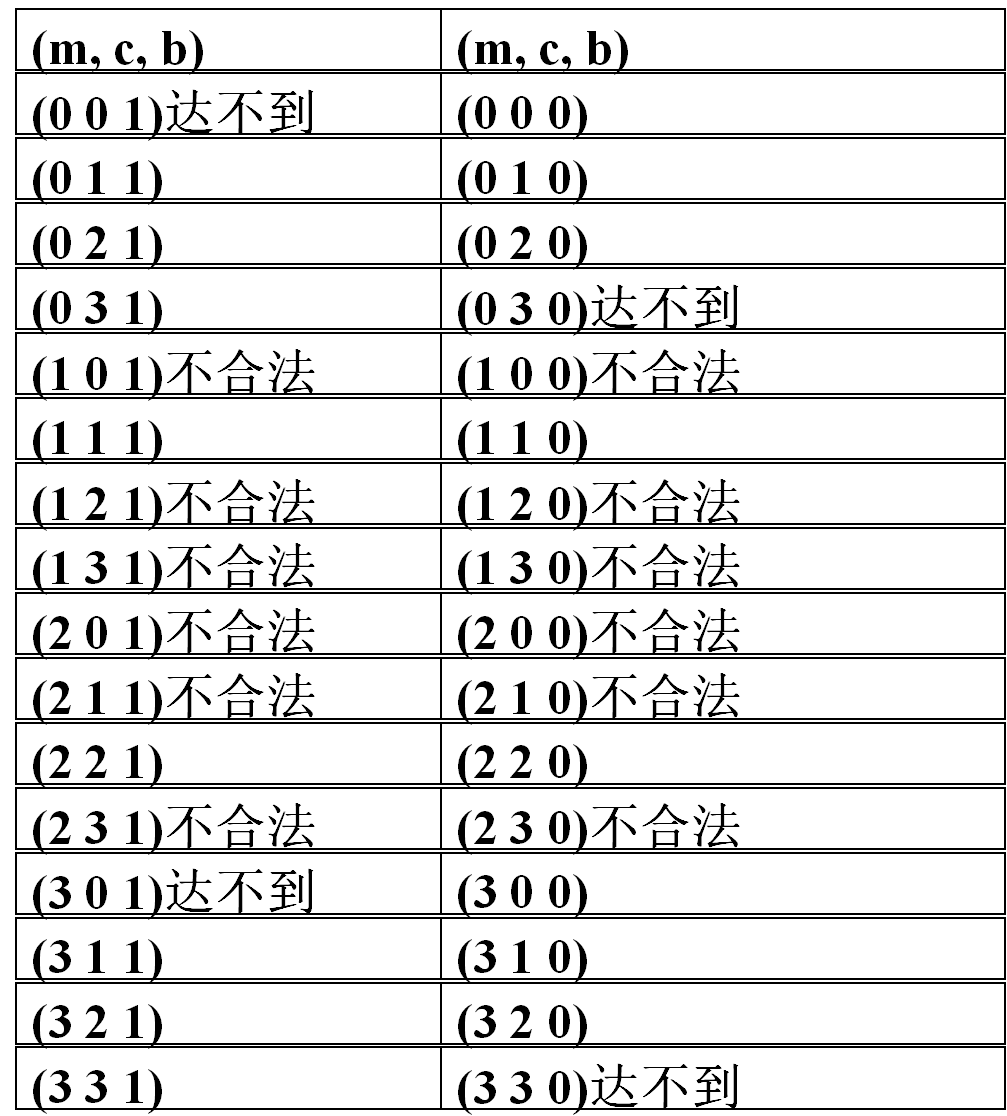
状态空间具体描述
3.2操作集
定义:Pmc操作:从左岸划向右岸
Qmc操作:从右岸划向左岸
船上人数组合(m,c)共5种(1,0),(1,1),(2,0),(0,1),(0,2)
∵每一种船上的人数组合同时对应P,Q二种操作
∴系统共有5×2=10种操作(规则)
如:P10:if (ML,CL,BL=1) then (ML-1,CL,BL-1)
如果船在左岸,那么一个传教士划船到右岸
Q01:if (ML,CL,BL=0) then (ML,CL+1,BL+1)
如果船在右岸,那么一个野人划船回到左岸
总共有10种操作
F={P10,P20, P11, P01, P02, Q 10, Q 20, Q 11, Q 01, Q 02}
P10 if( ML ,CL , BL=1 ) then ( ML–1 , CL , BL–1 )
P01 if( ML ,CL , BL=1 ) then ( ML , CL–1 , BL–1 )
P11 if( ML ,CL , BL=1 ) then ( ML–1 , CL–1 ,BL –1 )
P20 if( ML ,CL , BL=1 ) then ( ML–2 , CL , BL–1 )
P02 if( ML ,CL , BL=1 ) then ( ML , CL–2 , BL–1 )
Q10 if( ML ,CL , BL=0 ) then ( ML+1 , CL ,BL+1 )
Q01 if( ML ,CL , BL=0 ) then ( ML , CL+1 , BL+1 )
Q11 if( ML ,CL , BL=0 ) then ( ML+1 , CL +1,BL +1 )
Q20 if( ML ,CL , BL=0 ) then ( ML+2 , CL +2,BL +1 )
Q02 if( ML ,CL , BL=0 ) then ( ML , CL +2, BL+1 )
3.3控制策略
最短路径有4条,由11次操作构成。
(P11、Q10、P02、Q01、P20、Q11、P20、Q01、P02、Q01、P02)
(P11、Q10、P02、Q01、P20、Q11、P20、Q01、P02、Q10、P11)
(P02、Q01、P02、Q01、P20、Q11、P20、Q01、P02、Q01、P02)
(P02、Q01、P02、Q01、P20、Q11、P20、Q01、P02、Q10、P11)
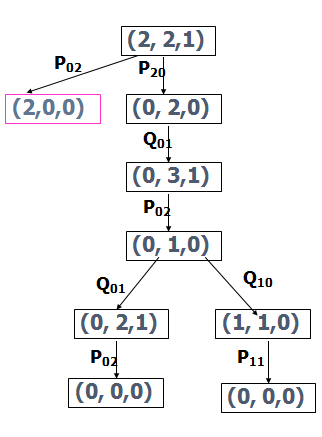
3.4状态空间图
状态空间图是一个有向图,图中的节点代表状态,节点之间的连线代表操作,箭头代表状态的转换方向。
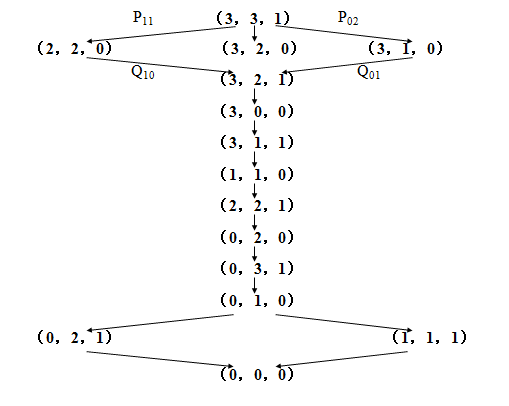
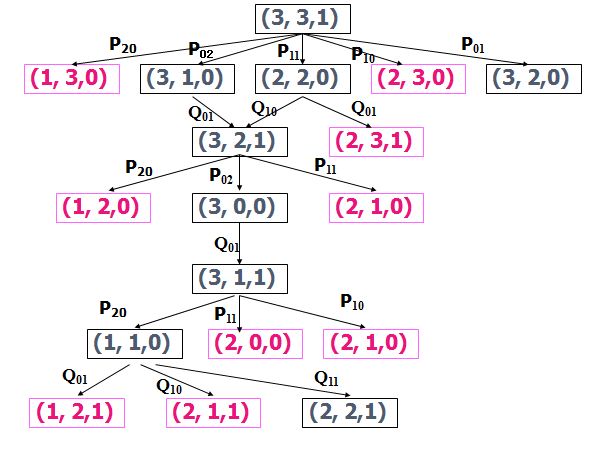
3.5状态空间的一般搜索过程
OPEN表:用于存放刚生成的节点
CLOSE表:用于存放将要扩展或已扩展的节点
1) 把初始节点S0放入OPEN表,并建立只含S0的图,记为G
OPEN:=S0,G:=G0(G0=S0)
2) 检查OPEN表是否为空,若为空则问题无解,退出
LOOP:IF(OPEN)=() THEN EXIT(FAIL)
3) 把OPEN表的第一个节点取出放入CLOSE表,记该节点为节点n
N:=FIRST(OPEN),REMOVE(n,OPEN),ADD(n,CLOSE)
4) 观察节点n是否为目标节点,若是,则求得问题的解,退出
IF GOAL(n) THEN EXIT(SUCCESS)
5) 扩展节点n,生成一组子节点.把其中不是节点n先辈的那些子节点记作集合M,并把这些节点作为节点n的子节点加入G中.
EXPAND(n)-->M(mi),G:=ADD(mi,G)
针对M中子节点的不同情况,分别进行如下处理
对于那些未曾在G中出现过的M成员设置一个指向父节点(n)的指针,并把它放入OPEN表
对于那些先前已在G中出现过的M成员,确定是否要修改指向父节点的指针
对于那些先前已在G中出现,并且已经扩展了的M成员,确定是否需要修改其后继结点指向父节点的指针
6) 按某种搜索策略对OPEN表中的节点进行排序
7) 转第2步
针对本题,设置OPEN、CLOSED两个队列分别存放待扩展节点和已扩展节点;
对每个生成的新节点,要检查上述两表中是否已存在,是否是非法节点;
(合法节点满足:
ML=0||ML=3||ML=CL)
每扩展一个节点应记录产生合法后继节点的操作,以便最后给出操作序列;
4.程序设计
4.1数据结构
节点状态用列表(m,c,b)表示,其中m表示传教士在左岸的人数; c表示野人在左岸的人数;b表示船是否在左岸,当b=1时,表示船在左岸,当b=0时,表式船在右岸。
初始状态: (3,3,1)
目标状态: (0,0,0)
操作算子: 船上人数组合(m,c)共5种 (1,0),(1,1),(2,0),(0,1),(0,2)
因此算法有10种
1) 从右岸向左岸过1个传教士,0个野人
2) 从右岸向左岸过1个传教士,1个野人
3) 从右岸向左岸过2个传教士,0个野人
4) 从右岸向左岸过0个传教士,1个野人
5) 从右岸向左岸过0个传教士,2个野人
6) 从左岸向右岸过1个传教士,0个野人
7) 从左岸向右岸过1个传教士,1个野人
8) 从左岸向右岸过2个传教士,0个野人
9) 从左岸向右岸过0个传教士,1个野人
10) 从左岸向右岸过0个传教士,2个野人
状态节点:
typedef struct st
{
int m; //传教士
int c; //野人
int b; //船左
}state; //状态
将有效的状态节点存储在树中
Tree 中的节点
typedef struct hnode
{
state s;
struct hnode *left;
struct hnode *right;
}node;
Open表,closed表 用队列存储
//定义队列中的节点
typedef structQueuenode
{
node * np;
struct Queuenode*next;
}Qnode; //队列中节点
//定义队列
typedef structQueue
{
Qnode *front;
Qnode *rear;
}queue;
4.2代码设计
4.2.1面向对象的迭代方法
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 typedef struct MCNode
5 {
6 int m;
7 int c;
8 int b;
9 int num;
10 struct MCNode *next;
11 struct MCNode *last;
12 }MCNode;
13
14 class List
15 {
16 private:
17 MCNode *head;
18 MCNode *rear;
19 MCNode *current;
20 public:
21 List();
22 friend bool operator==(MCNode &node1,MCNode &node2);
23 void push_front(MCNode cNode);
24 void push_back(MCNode cNode);
25 void pop_front();
26 void pop_back();
27 MCNode &front();
28 MCNode &back();
29 void print_list();
30 bool hit_target(MCNode &cNode);
31 bool legal(MCNode &cNode);
32 bool empty();
33 bool exist(MCNode &cNode);
34 };
35
36 List::List()
37 {
38 head=new MCNode();
39 rear=head;
40 head->m=3;
41 head->c=3;
42 head->b=1;
43 head->num=0;
44 head->last=NULL;
45 head->next=NULL;
46 }
47
48 bool operator==(MCNode &node1,MCNode &node2)
49 {
50 if(node1.m==node2.m&&node1.c==node2.c&&node1.b==node2.b)
51 return true;
52 else
53 return false;
54 }
55
56 void List::push_front(MCNode cNode)
57 {
58 (*head).last=new MCNode();
59 head->last->next=head;
60 head=head->last;
61 head->m=cNode.m;
62 head->c=cNode.c;
63 head->b=cNode.b;
64 head->num=cNode.num;
65 head->last=NULL;
66 }
67
68 void List::push_back(MCNode cNode)
69 {
70 (*rear).next=new MCNode();
71 rear->next->last=rear;
72 rear=rear->next;
73 rear->m=cNode.m;
74 rear->c=cNode.c;
75 rear->b=cNode.b;
76 rear->num=cNode.num;
77 rear->next=NULL;
78 }
79
80 void List::pop_front()
81 {
82 if(head->next!=NULL)
83 {
84 head=head->next;
85 head->last=NULL;
86 }
87 else
88 {
89 head=NULL;
90 rear=NULL;
91 }
92 }
93
94 void List::pop_back()
95 {
96 if(rear->last!=NULL)
97 {
98 rear=rear->last;
99 rear->next=NULL;
100 }
101 else
102 {
103 head=NULL;
104 rear=NULL;
105 }
106 }
107
108 MCNode &List::front()
109 {
110 return *head;
111 }
112
113 MCNode &List::back()
114 {
115 return *rear;
116 }
117
118 void List::print_list()
119 {
120 MCNode current;
121 current=*head;
122 while(true)
123 {
124 cout<<current.num<<","<<current.m<<","<<current.c<<","<<current.b<<endl;
125 if(current.next==NULL)
126 break;
127 else
128 {
129 current.c=current.next->c;
130 current.m=current.next->m;
131 current.b=current.next->b;
132 current.num=current.next->num;
133 current.next=current.next->next;
134 }
135 }system("pause");
136 }
137
138 bool List::hit_target(MCNode &cNode)
139 {
140 MCNode goalNode;
141 goalNode.m=0;
142 goalNode.c=0;
143 goalNode.b=0;
144 if(cNode==goalNode)
145 return true;
146 else
147 return false;
148 }
149
150 bool List::legal(MCNode &cNode)
151 {
152 if(cNode.m>=0&&cNode.m<=3&&cNode.c>=0&&cNode.c<=3)
153 {
154 if((cNode.m==cNode.c)||(cNode.m==3)||(cNode.m==0))
155 return true;
156 else
157 return false;
158 }
159 else
160 return false;
161 }
162
163 bool List::empty()
164 {
165 if(head==NULL)
166 return true;
167 else
168 return false;
169 }
170
171 bool List::exist(MCNode &cNode)
172 {
173 MCNode *current;
174 current=head;
175 while(current!=NULL)
176 {
177 if(cNode.b==current->b&&
178 cNode.c==current->c&&cNode.m==current->m)
179 return true;
180 else
181 current=current->next;
182 }
183 return false;
184 }
185
186 void print(MCNode &cNode)
187 {
188 cout<<"节点输出:"<<endl;
189 cout<<cNode.num<<" "<<cNode.m<<","<<cNode.c<<","<<cNode.b<<endl;
190 system("pause");
191 }
192
193 void expandNode(List &opend,List &closed)
194 {
195 int ii;
196 MCNode cNode=opend.front();
197 MCNode node[5];
198 if(cNode.b==1)
199 {
200 for(ii=0;ii<5;ii++)
201 {
202 node[ii].b=0;
203 }
204 node[0].m=cNode.m-1;
205 node[0].c=cNode.c;
206 node[1].m=cNode.m;
207 node[1].c=cNode.c-1;
208 node[2].m=cNode.m-1;
209 node[2].c=cNode.c-1;
210 node[3].m=cNode.m-2;
211 node[3].c=cNode.c;
212 node[4].m=cNode.m;
213 node[4].c=cNode.c-2;
214 }
215 else
216 {
217 for(ii=0;ii<5;ii++)
218 {
219 node[ii].b=1;
220 }
221 node[0].m=cNode.m+1;
222 node[0].c=cNode.c;
223 node[1].m=cNode.m;
224 node[1].c=cNode.c+1;
225 node[2].m=cNode.m+1;
226 node[2].c=cNode.c+1;
227 node[3].m=cNode.m+2;
228 node[3].c=cNode.c;
229 node[4].m=cNode.m;
230 node[4].c=cNode.c+2;
231 }
232 for(ii=opend.front().num;ii!=5;ii++)
233 {
234 opend.front().num++;
235 if(opend.legal(node[ii])&&!opend.exist(node[ii]))
236 {
237 opend.push_front(node[ii]);
238 opend.front().num=0;
239 closed.push_back(opend.front());
240 return;
241 }
242 }
243 }
244
245 void proceeding(List &opend,List &closed)
246 {
247 int ii;
248 int NUM=0;
249 while(!opend.empty())
250 {
251 //opend.print_list();
252 if(opend.hit_target(opend.front()))
253 {
254 NUM++;
255 cout<<"The "<<NUM<<"st route is found!"<<endl;
256 closed.print_list();
257 cout<<endl;
258 opend.pop_front();
259 closed.pop_front();
260 }
261 else if(opend.front().num!=5)
262 {
263 expandNode(opend,closed);
264 }
265 else
266 {
267 opend.pop_front();
268 closed.pop_back();
269 }
270 }
271 }
272
273 int main(int argc,char** argv)
274 {
275 List opend,closed;
276 proceeding(opend,closed);
277 system("pause");
278 return 0;
279 }
4.2.2单函递归法
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 #define MAX 1024
5
6 typedef struct rule
7 {
8 int missionary;
9 int savage;
10 }Rule;
11
12 typedef struct node
13 {
14 int missionary;
15 int savage;
16 int boat;
17 int direct;
18 }Node;
19
20 typedef struct sequenceStack
21 {
22 Node data[MAX];
23 int top;
24 }SequenceStack;
25
26 int NUM=0;
27
28 bool stack_empty(SequenceStack &stack)
29 {
30 if(stack.top==-1)
31 {
32 return true;
33 }
34 return false;
35 }
36
37 bool stack_full(SequenceStack &stack)
38 {
39 if(stack.top==MAX-1)
40 {
41 return true;
42 }
43 return false;
44 }
45
46 bool stack_push(SequenceStack &stack,Node &node)
47 {
48 if(stack_full(stack))
49 {
50 cout<<"The stack is full,pushing failed!"<<endl;
51 return false;
52 }
53 stack.top++;
54 stack.data[stack.top].missionary=node.missionary;
55 stack.data[stack.top].savage=node.savage;
56 stack.data[stack.top].boat=node.boat;
57 stack.data[stack.top].direct=node.direct;
58 return true;
59 }
60
61 bool stack_pop(SequenceStack &stack)
62 {
63 if(stack_empty(stack))
64 {
65 cout<<"The stack is empty,poping failed!"<<endl;
66 return false;
67 }
68 stack.top--;
69 return true;
70 }
71
72 bool node_reach(Node &node)
73 {
74 if(node.missionary==0&&node.savage==0&&node.boat==0)
75 {
76 return true;
77 }
78 return false;
79 }
80
81 bool node_equal(Node &node1,Node &node2)
82 {
83 if(node1.missionary==node2.missionary&&
84 node1.savage==node2.savage&&
85 node1.boat==node2.boat)
86 {
87 return true;
88 }
89 return false;
90 }
91
92 bool node_visited(SequenceStack &stack,Node &node)
93 {
94 int ii;
95 for(ii=0;ii<=stack.top;ii++)
96 {
97 if(node_equal(stack.data[ii],node))
98 {
99 return true;
100 }
101 }
102 return false;
103 }
104
105 void stack_print(SequenceStack &stack)
106 {
107 int ii;
108 cout<<"The "<<++NUM<<"st method is:"<<endl;
109 for(ii=0;ii<=stack.top;ii++)
110 {
111 cout<<"("<<stack.data[ii].missionary;
112 cout<<","<<stack.data[ii].savage;
113 cout<<","<<stack.data[ii].boat<<")"<<endl;
114 }
115 cout<<endl;
116 system("pause");
117 }
118
119 void rule_print(int ruleset_num,Rule *rule)
120 {
121 int ii;
122 for(ii=0;ii<ruleset_num;ii++)
123 {
124 cout<<"("<<rule[ii].missionary<<","<<rule[ii].savage<<")"<<endl;
125 }
126 cout<<endl;
127 system("pause");
128 }
129
130 void rule_set(int &sample,int &capacity,Rule *rule)
131 {
132 int ii,ij,ik=0;
133 for(ii=0;ii<sample;ii++)
134 {
135 for(ij=0;ij<sample;ij++)
136 {
137 if(ii==0&&ij==0)
138 {
139 continue;
140 }
141 if(ii+ij<=capacity)
142 {
143 rule[ik].missionary=ii;
144 rule[ik++].savage=ij;
145 }
146 }
147 }
148 }
149
150 int ruleset_num_get(int &sample,int &capacity)
151 {
152 int ii,ij,num=0;
153 for(ii=0;ii<sample;ii++)
154 {
155 for(ij=0;ij<sample;ij++)
156 {
157 if(ii==0&&ij==0)
158 {
159 continue;
160 }
161 if(ii+ij<=capacity)
162 {
163 num++;
164 }
165 }
166 }
167 return num;
168 }
169
170 void init(SequenceStack &stack,int &ruleset_num,int &sample,int &capacity)
171 {
172 cout<<"Please enter the initial number of savages and missionaries:"<<endl;
173 cin>>sample;
174 cout<<"Please enter the ship's carrying capacity:"<<endl;
175 cin>>capacity;
176 ruleset_num=ruleset_num_get(sample,capacity);
177 cout<<"nThere is a total of "<<ruleset_num<<" sets of rules:"<<endl;
178 stack.top=0;
179 stack.data[stack.top].missionary=sample;
180 stack.data[stack.top].savage=sample;
181 stack.data[stack.top].boat=1;
182 stack.data[stack.top].direct=0;
183 }
184
185 void processing(SequenceStack &stack,Rule *rule,int &ruleset_num,int &sample)
186 {
187 Node cNode;
188 if(node_reach(stack.data[stack.top]))
189 {
190 stack_print(stack);
191 }
192 else
193 {
194 while(stack.data[stack.top].direct<ruleset_num)
195 {
196 if(stack.data[stack.top].boat==1)
197 {
198 cNode.missionary=stack.data[stack.top].missionary-
199 rule[stack.data[stack.top].direct].missionary;
200 cNode.savage=stack.data[stack.top].savage-
201 rule[stack.data[stack.top].direct].savage;
202 cNode.boat=0;
203 cNode.direct=0;
204 if(node_visited(stack,cNode)==false&&
205 (cNode.missionary==cNode.savage||
206 cNode.missionary==0||cNode.missionary==sample)&&
207 (cNode.missionary>=0)&&(cNode.missionary<=sample)&&
208 (cNode.savage>=0)&&(cNode.savage<=sample))
209 {
210 stack_push(stack,cNode);
211 processing(stack,rule,ruleset_num,sample);
212 stack_pop(stack);
213 }
214 }
215 else
216 {
217 cNode.missionary=stack.data[stack.top].missionary+
218 rule[stack.data[stack.top].direct].missionary;
219 cNode.savage=stack.data[stack.top].savage+
220 rule[stack.data[stack.top].direct].savage;
221 cNode.boat=1;
222 cNode.direct=0;
223 if(node_visited(stack,cNode)==false&&
224 (cNode.missionary==cNode.savage||
225 cNode.missionary==0||cNode.missionary==sample)&&
226 (cNode.missionary>=0)&&(cNode.missionary<=sample)&&
227 (cNode.savage>=0)&&(cNode.savage<=sample))
228 {
229 stack_push(stack,cNode);
230 processing(stack,rule,ruleset_num,sample);
231 stack_pop(stack);
232 }
233 }
234 stack.data[stack.top].direct++;
235 }
236 }
237 }
238
239 int main(int argc,char **argv)
240 {
241 SequenceStack stack;
242 Rule *rule;
243 int ruleset_num,sample,capacity;
244 init(stack,ruleset_num,sample,capacity);
245 rule=new Rule[ruleset_num];
246 rule_set(sample,capacity,rule);
247 rule_print(ruleset_num,rule);
248 processing(stack,rule,ruleset_num,sample);
249 system("pause");
250 return 0;
251 }
4.2.3双函递归法
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #define MAXSIZE 1024
4
5 typedef struct Rule
6 {
7 int mm;
8 int cc;
9 }Rule;
10 Rule rule[5]={{1,0},{0,1},{1,1},{2,0},{0,2}};
11
12 typedef struct Node
13 {
14 int m;
15 int c;
16 int b;
17 }Node;
18
19 typedef Node elemtype;
20
21 typedef struct SequenStack
22 {
23 elemtype data[MAXSIZE];
24 int top;
25 }SequenStack;
26
27 int NUM=0;
28
29 int visited(SequenStack *open,Node newnode)
30 {
31 int ii=0;
32 if(open->top!=-1)
33 {
34 for(ii=0;ii!=open->top;ii++)
35 {
36 if(newnode.m==open->data[ii].m&&
37 newnode.c==open->data[ii].c&&
38 newnode.b==open->data[ii].b)
39 {
40 return 1;
41 }
42 }
43 }
44 return 0;
45 }
46
47 int legal(SequenStack *open,Node newnode)
48 {
49 int i=visited(open,newnode);
50 if(i==0)
51 {
52 if(newnode.m>=0&&newnode.m<=3&&newnode.c>=0&&newnode.c<=3)
53 {
54 if(newnode.m==0||newnode.m==3||newnode.m==newnode.c)
55 {
56 return 1;
57 }
58 }
59 }
60 return 0;
61 }
62
63 int Pop_SequenStack(SequenStack *S)
64 {
65 if(S->top==-1)
66 {
67 printf("The linear list is empty,poping to stack failed!n");
68 return 0;
69 }
70 else
71 {
72 S->top--;
73 return 1;
74 }
75 }
76
77 int Push_SequenStack(SequenStack *S,Node node)
78 {
79 if(S->top>=MAXSIZE-1)
80 {
81 printf("The linear list is full,pushing to stack failed!n");
82 return 0;
83 }
84 S->top++;
85 S->data[S->top]=node;
86 return 1;
87 }
88
89 void print_result(SequenStack *open)
90 {
91 int ii;
92 printf("第%d种:n",++NUM );
93 if(open->top!=-1)
94 {
95 for(ii=0;ii<=open->top;ii++)
96 {
97 printf("(%d,%d,%d)n",open->data[ii].m,
98 open->data[ii].c,open->data[ii].b);
99 }
100 }
101 printf("n");
102 system("pause");
103 }
104
105 void print(SequenStack *open)
106 {
107 int ii;
108 if(open->top!=-1)
109 {
110 for(ii=0;ii<=open->top;ii++)
111 {
112 printf("(%d,%d,%d)-->",open->data[ii].m,
113 open->data[ii].c,open->data[ii].b);
114 }
115 }
116 printf("n");
117 system("pause");
118 }
119 void DFS(SequenStack *open,Node newnode);
120
121 void processing(SequenStack *open,Node newnode)
122 {
123 int ii,flag;
124 Node node;
125 node.m=newnode.m;
126 node.c=newnode.c;
127 node.b=newnode.b;
128 if(node.b==1)
129 {
130 for(ii=0;ii<5;ii++)
131 {
132 node.m=newnode.m-rule[ii].mm;
133 node.c=newnode.c-rule[ii].cc;
134 node.b=0;
135 flag=legal(open,node);
136 if(flag==1)
137 {
138 Push_SequenStack(open,node);
139 DFS(open,node);
140 Pop_SequenStack(open);
141 }
142 }
143 }
144 else
145 {
146 for(ii=0;ii<5;ii++)
147 {
148 node.m=newnode.m+rule[ii].mm;
149 node.c=newnode.c+rule[ii].cc;
150 node.b=1;
151 flag=legal(open,node);
152 if(flag==1)
153 {
154 Push_SequenStack(open,node);
155 DFS(open,node);
156 Pop_SequenStack(open);
157 }
158 }
159 }
160 }
161
162 void DFS(SequenStack *open,Node node)
163 {
164 if(node.m==0&&node.c==0&&node.b==0)
165 {
166 print_result(open);
167 }
168 else
169 {
170 processing(open,node);
171 }
172 }
173
174 Node init_node()
175 {
176 Node node;
177 node.m=3;
178 node.c=3;
179 node.b=1;
180 return node;
181 }
182
183 SequenStack * Init_open()
184 {
185 SequenStack *open;
186 open=(SequenStack * )malloc(sizeof(SequenStack));
187 open->top=-1;
188 return open;
189 }
190
191 int main(int argc,char **argv)
192 {
193 SequenStack *open=Init_open();
194 Node node=init_node();
195 Push_SequenStack(open,node);
196 DFS(open,node);
197 system("pause");
198 return 0;
199 }
4.2.4类集框架迭代版
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector>
3 #include <list>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 typedef struct MCNode
7 {
8 int m;
9 int c;
10 int b;
11 int num;
12 }MCNode;
13
14 int NUM=0;
15
16 bool operator==(MCNode &m1,MCNode &m2)
17 {
18 if(m1.m==m2.m&&m1.c==m2.c&&m1.b==m2.b)
19 return true;
20 else
21 return false;
22 }
23
24 bool goal(MCNode &cNode)
25 {
26 MCNode goalNode;
27 goalNode.m=0;
28 goalNode.c=0;
29 goalNode.b=0;
30 if(cNode==goalNode)
31 return true;
32 else
33 return false;
34 }
35
36 bool legal(MCNode &cNode)
37 {
38 if(cNode.m>=0&&cNode.m<=3&&cNode.c>=0&&cNode.c<=3)
39 {
40 if((cNode.m==cNode.c)||(cNode.m==3)||(cNode.m==0))
41 return true;
42 else
43 return false;
44 }
45 else
46 return false;
47 }
48
49 bool visited(MCNode cNode,list<MCNode> &opend)
50 {
51 list<MCNode>::iterator it;
52 for(it=opend.begin();it!=opend.end();it++)
53 {
54 if(it->m==cNode.m&&it->c==cNode.c&&it->b==cNode.b)
55 return true;
56 }
57 return false;
58 }
59
60 void print_list(list<MCNode> &opend)
61 {
62 list<MCNode>::iterator it;
63 for(it=opend.begin();it!=opend.end();it++)
64 {
65 cout<<it->num<<","<<it->m<<","<<it->c<<","<<it->b<<endl;
66 }
67 system("pause");
68 }
69
70 void print_result(vector<MCNode> &closed)
71 {
72 vector<MCNode>::iterator it;
73 for(it=closed.begin();it!=closed.end();it++)
74 {
75 cout<<it->num<<","<<it->m<<","<<it->c<<","<<it->b<<endl;
76 }
77 cout<<endl;
78 system("pause");
79 }
80
81 void expandNode(list<MCNode> &opend,vector<MCNode> &closed)
82 {
83 int ii;
84 MCNode cNode=opend.front();
85 MCNode node[5];
86 if(cNode.b==1)
87 {
88 for(ii=0;ii<5;ii++)
89 {
90 node[ii].b=0;
91 }
92 node[0].m=cNode.m-1;
93 node[0].c=cNode.c;
94 node[1].m=cNode.m;
95 node[1].c=cNode.c-1;
96 node[2].m=cNode.m-1;
97 node[2].c=cNode.c-1;
98 node[3].m=cNode.m-2;
99 node[3].c=cNode.c;
100 node[4].m=cNode.m;
101 node[4].c=cNode.c-2;
102 }
103 else
104 {
105 for(ii=0;ii<5;ii++)
106 {
107 node[ii].b=1;
108 }
109 node[0].m=cNode.m+1;
110 node[0].c=cNode.c;
111 node[1].m=cNode.m;
112 node[1].c=cNode.c+1;
113 node[2].m=cNode.m+1;
114 node[2].c=cNode.c+1;
115 node[3].m=cNode.m+2;
116 node[3].c=cNode.c;
117 node[4].m=cNode.m;
118 node[4].c=cNode.c+2;
119 }
120 for(ii=opend.front().num;ii!=5;ii++)
121 {
122 opend.front().num++;
123 if(legal(node[ii])&&!visited(node[ii],opend))
124 {
125 opend.push_front(node[ii]);
126 opend.front().num=0;
127 closed.push_back(opend.front());
128 return;
129 }
130 }
131 }
132
133 void proceeding(list<MCNode> &opend,vector<MCNode> &closed)
134 {
135 int ii;
136 while(!opend.empty())
137 {
138 //print_list(opend);
139 if(goal(opend.front()))
140 {
141 NUM++;
142 cout<<"The "<<NUM<<"st route is found!"<<endl;
143 print_result(closed);
144 opend.pop_front();
145 closed.pop_back();
146 }
147 else if(opend.front().num!=5)
148 {
149 expandNode(opend,closed);
150 }
151 else
152 {
153 opend.pop_front();
154 closed.pop_back();
155 }
156 }
157 }
158
159 MCNode initNode()
160 {
161 MCNode cNode;
162 cNode.m=3;
163 cNode.c=3;
164 cNode.b=1;
165 cNode.num=0;
166 return cNode;
167 }
168
169 int main(int argc,char** argv)
170 {
171 list<MCNode> opend;
172 vector<MCNode> closed;
173 opend.push_front(initNode());
174 proceeding(opend,closed);
175 system("pause");
176 return 0;
177 }
本文来源于互联网:野人传教士过河问题

108 条评论 “野人传教士过河问题”